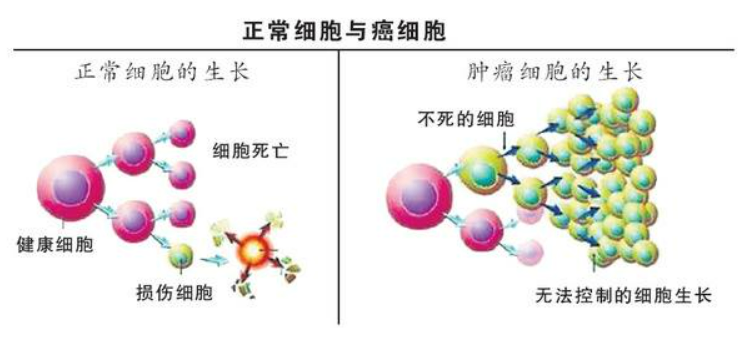
Cancer cells usually originate from normal cells. Cancer cells are formed by the mutation of normal cells. This is due to errors in the DNA replication process, resulting in gene mutations that turn normal cells into cancer cells. Cancer is the uncontrolled proliferation of mutated cells. A condition that continues to grow, disrupting normal physiology throughout the body. The English word Cancer comes from the Latin word “crab”. Like a crab, cancer stretches its terrible “claws” and constantly invades healthy tissues and organs in the body.
Normally, the immune system clears these cancer cells. But if your immune system is weakened, or if cancer cells escape the immune system’s surveillance, the cancer cells continue to grow and eventually become difficult to repair. Medical institutions classify cancers by their site of origin (where the original cells first appeared) or by the type of tissue at the site of origin. If classified according to the primary site, cancer can be divided into lung cancer, brain cancer, etc.; if classified according to the tissue type of the primary site, cancer can be divided into six major categories: carcinoma, sarcoma, myeloma, leukemia, lymphoma and mixed type of cancer.

