Fractures occur when a bone is struck or crushed with more force than it can handle, usually by accident. Fracture patients often experience local pain, swelling, inconvenience of movement after trauma, skeletal deformity, and abnormal movement. In addition, serious accidents can lead to multiple fractures or shock, which can be life-threatening. There are three main reasons for fractures:
1. Direct violence – force applied directly to part of the bone that results in a fracture in the injured area, usually with varying degrees of soft tissue damage, for example, if the wheel hits the lower leg, a fracture occurs at the point of impact.
2. Indirect Violence – Indirect pressure can also cause fractures, compression or burst fractures of the vertebral bodies occur when a person falls from a height and lands on their feet.
3. Cumulative Strain Injury – Long-term, repetitive, minor direct or indirect injuries can lead to fractures in specific parts of the limb, also known as fatigue fractures, and some people may be prone to fractures from long walks.
In addition, some fractures can lead to serious complications, which can lead to amputation and death in the most severe cases. Complications of fractures fall into two categories: early and delayed. Early complications include shock, fat embolism, compartment syndrome, deep vein thrombosis, and infection; delayed complications include delayed bone union and nonunion, complex regional pain syndrome, and heterotrophic ossification. There are four recommendations for therapy to accelerate bone repair:
1. Physiotherapy – The ultimate goal of helping a fracture is to restore maximum function of the injured limb, therefore, there are three very important basic principles: repositioning, immobilization, and functional exercise.
2. Focus on your diet – As a fracture patient, your diet should include vegetables, fruits, protein, and water. In particular, calcium, vitamin D, and protein are important in the bone healing process, so make sure you focus on food sources rich in these nutrients, such as leafy vegetables, broccoli, fish, meat, yogurt, nuts, and seeds.
3. Quit smoking – People who smoke may experience delayed bone healing, and sometimes, this can even lead to the development of non-union fractures or longer periods of healing.
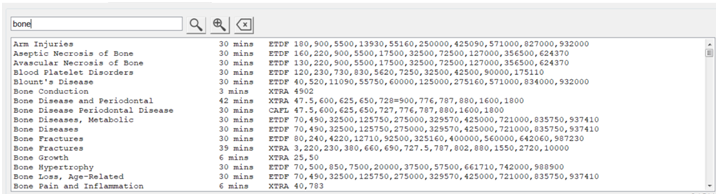
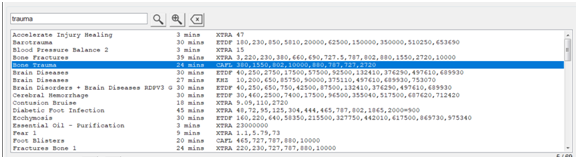
4. Spooky2 Frequency Therapy – We can use Spooky2 to help accelerate fracture healing, on Spooky2 Generator-X or -XM, search with “bone” or “trauma” as a keyword, and load some bone trauma programs, as shown below , perform frequency therapy.